
Along the boundaries of these plates are zones of interaction, where plates can meet and create a plate margin.
There are a number of different types of plate margins; and it is along these that physical processes can have an affect on the landscape.
Convergent (Destructive plate) boundaries:
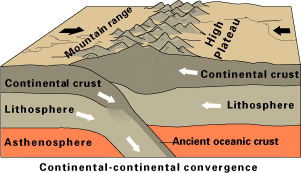
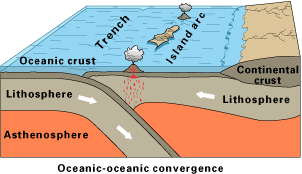
Destructive plate boundaries can occur along any of the three plate margins (with both oceanic and continental crust). The three pictures below show the processes that occur along a destructive plate boundary.
As this diagram shows, when two continental crusts collide, fold mountains are created, altering the landscape of a country. An example of this is the Himalayas.
As one plate submerges under another, the friction, pressure and heat can cause both earthquakes and volcanoes; both of which can lead to changes in the landscape.
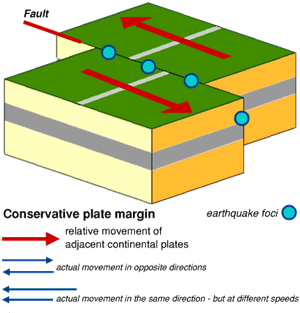
Conservative (Transform) plate boundaries:
Conservative plate boundaries occur when two plates are rubbing alongside each other, such is the case of the San Andreas fault in California. The friction and pressure built up as the plates travel horizontally alongside each other can cause earthquakes.
Divergent (Constructive) plate boundaries:
Constructive plate boundaries occur when two plates are pulling away from each other, creating a space where new material is created. Along these place boundaries, both earthquakes and volcanoes can happen. Also, mid ocean ridges are often formed, as is the case in the Atlantic ocean, as the picture below portrays.

Tectonic processes, as a physical process, can lead to change in places, landscapes and societies. They can greatly affect populations and are difficult to predict, prevent and manage.
If you would like to find out more about this topic please follow the link to a great page about all of these concepts... http://www.geologyrocks.co.uk/tutorials/plate_tectonics_introduction.
No comments:
Post a Comment